ACE –
Does that mean anything to you? For some it might conjure up the lyrics of an old George Straight song that says, “You’ve got to have an ace in the hole.” For others it brings images of poker games and winning hands. For others, names of all-star professional baseball pitchers. For others, the experience of serving in tennis and never getting a volley back. Maybe for you, it’s the terminology for someone who is always seemingly ahead – “He’s holding all the aces.”
But how many of you saw ACE and thought about difficult childhood experiences? I’m guessing not very many of you. This past week I had the opportunity to sit in a training which discussed trauma informed care. As part of that discussion, the ACEs were mentioned.
So, what are the ACEs?
ACEs in this context stands for Adverse Childhood Experiences. These are experiences that occur before the age of 18 that have a dramatic impact on how we live, function, and make decisions as an adult. The CDC-Kaiser Permanente Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) Study began in the mid-1990s and continued through 2015 and has consistently shown the impact of childhood experiences on adult functioning. Let’s take a minute to look at what was studied and the major findings.
The ACE Study looked at the occurrence of 10 major childhood experiences, which are typically divided into 3 main categories.
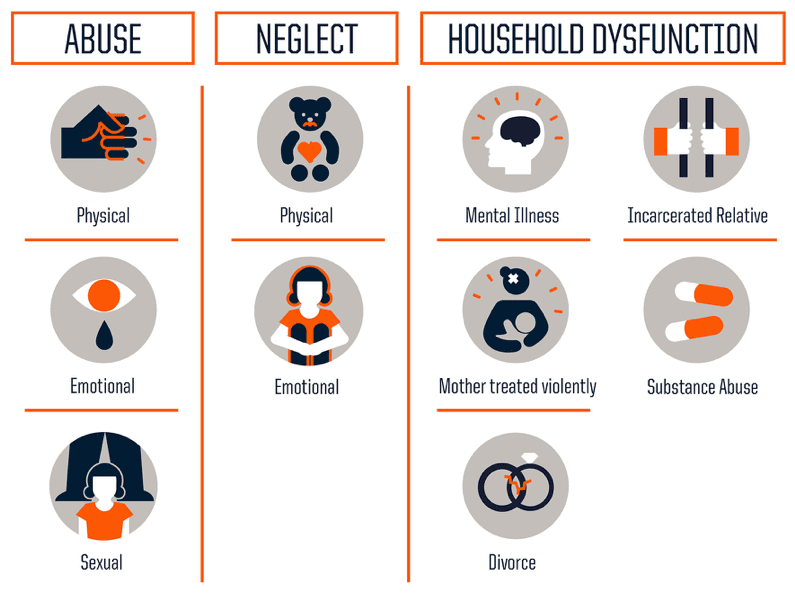 Source: https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2015/03/02/387007941/take-the-ace-quiz-and-learn-what-it-does-and-doesnt-mean
Source: https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2015/03/02/387007941/take-the-ace-quiz-and-learn-what-it-does-and-doesnt-mean
What It Said
According to the CDC, Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) are common. So common that almost 2/3 of participants reported at least one ACE, and more than 20% reported three or more ACEs. – Pause for a minute – that is statistically the majority of people that you meet every day. That is 1 in 5 who have had multiple significant experiences – most of which we don’t like to talk about.
So what does that mean? Per the CDC, as the number of ACEs increases, so does likelihood of the risk for the following:
- Alcoholism and alcohol abuse
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Depression
- Health-related quality of life
- Illicit drug use
- Heart disease
- Liver disease
- Poor work performance
- Financial stress
- Risk for intimate partner violence
- Multiple sexual partners
- Sexually transmitted diseases
- Smoking
- Suicide attempts
- Unintended pregnancies
- Early initiation of smoking
- Early initiation of sexual activity
- Adolescent pregnancy
- Risk for sexual violence
- Poor academic achievement
It covers it all – health problems, increased risky behaviors and a decreased life potential. It also leads to an increase likelihood of premature death.
Look at the list above again and let’s talk about students – especially high school students. Often, we as parents, youth workers, teachers, and Teen Life Facilitators spend a great deal of time talking about poor grades, teenage pregnancy, suicide attempts, self-injury behaviors, depression, anxiety, drug and alcohol use/abuse. But do we stop to take the time to think about what experiences might have contributed to these decisions? When we are feeling frustrated, do we see the behavior as defiance or a coping skill?
So now that we know what the ACEs are and what the research shows, what in the world do we do?
Build relationships.
According to Dr. Karyn Purvis, “The child with a history of loss, trauma, or abuse has no hope of healing without a nurturing relationship.” The presence of safe, stable, and nurturing relationships can greatly increase resiliency among children and youth who have experienced multiple ACEs.
Are you willing to look past the hard choices, to look past the mistakes, in order to see the experiences that have impacted the students in our lives? And when you do, are you willing to stick it out to connect and empower youth to overcome?
***For More Information about The CDC ACE Study can be found here and here. More information about the ACEs in general can be found here. More information about Dr. Karyn Purvis and her Trust Based Relational Intervention can be found here.




















